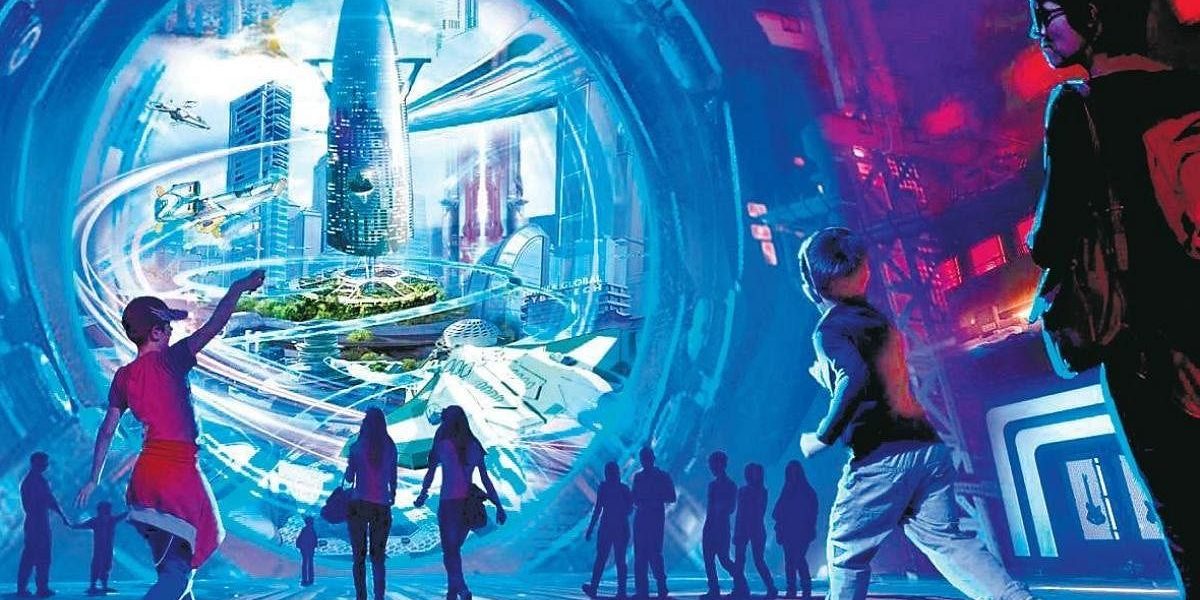
The metaverse, a burgeoning concept teetering on the edge of science fiction and imminent reality, has captured the imagination of tech giants, investors, and everyday users alike. Envisioned as a network of interconnected virtual worlds, the metaverse promises a paradigm shift in the way we interact, consume content, and conduct business. But how exactly will these virtual worlds be built? What are the building blocks, the bricks and bytes, that will give form to our digital avatars and the immersive experiences they’ll inhabit?
Core technologies shaping the development of the metaverse, exploring the tools and techniques that will bring these virtual worlds to life. We’ll unpack the fundamentals of metaverse development, highlighting the key areas that will define the construction and functionality of these digital spaces.
The Foundational Layers
The metaverse isn’t a singular entity; it’s a constellation of interconnected experiences. At its core, metaverse development relies on several foundational layers:
Real-time 3D Engines:
These engines, familiar to the gaming world (e.g., Unity, Unreal Engine), are responsible for rendering the visual aspects of the metaverse, creating the 3D landscapes, objects, and avatars users will interact with. They handle lighting, physics simulations, and real-time interactions, ensuring a smooth and immersive experience.
Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain’s core strengths – decentralization, security, and immutability – make it a natural fit for the metaverse. Blockchain can be used for secure digital asset ownership, facilitating the creation and ownership of virtual land, items, and avatars within the metaverse. It also enables the development of metaverse economies, allowing users to buy, sell, and trade virtual goods and services.
Cloud Computing:
The metaverse’s vast scale necessitates a robust infrastructure. Cloud computing platforms provide the on-demand scalability and processing power required to render complex virtual worlds and support a large number of concurrent users. Cloud-based solutions also ensure data storage and accessibility across different devices and locations.
Building the Metaverse: Key Technologies
On top of these foundational layers, several key technologies will play a crucial role in shaping the construction of the metaverse:
Extended Reality (XR):
XR, encompassing virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), will be the primary interface for accessing the metaverse. VR headsets will transport users entirely into virtual worlds, while AR overlays will integrate digital elements into the physical world. MR will blend the two, creating hybrid environments.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI will power various aspects of the metaverse, from creating intelligent non-player characters (NPCs) to personalizing user experiences. AI can be used for natural language processing, enabling realistic interactions between avatars and the virtual environment. Additionally, AI can personalize content and recommendations within the metaverse based on user preferences and behavior.
High-Fidelity Audio:
Spatial audio will be crucial for replicating real-world soundscapes and creating a sense of presence in the metaverse. Imagine the immersive difference between hearing a generic gunshot sound and a spatially accurate one that whizzes past your virtual ear. High-fidelity audio will heighten the realism and emotional impact of metaverse experiences.
Haptics and Force Feedback:
These technologies will add another layer of immersion by simulating touch sensations. Imagine feeling the texture of a virtual object you pick up in the metaverse, or the recoil of a virtual weapon. Haptics will blur the lines between the physical and virtual worlds, making interactions within the metaverse even more realistic.
Open vs. Closed Metaverse
A critical question in metaverse development is the degree of openness and interoperability. Will the metaverse be a collection of siloed, isolated experiences, or will it be a web of interconnected virtual worlds?
-
Closed Metaverse: In a closed metaverse, each platform operates as its own independent universe, with limited or no interaction between them. Users would be restricted to the specific virtual world offered by each platform, unable to carry their avatars or digital assets across different experiences. This approach could lead to fragmentation and limit the overall potential of the metaverse.
-
Open Metaverse: An open metaverse strives for interoperability, allowing users to seamlessly move between different virtual worlds with their avatars and digital goods intact. This would necessitate common standards and protocols for data exchange and communication between platforms. An open metaverse fosters a more expansive and interconnected digital landscape.
The current development trajectory of the metaverse leans towards an open architecture. Interoperability standards are being actively explored by industry groups, with the goal of creating a more unified and user-friendly experience.
The Future of Metaverse Development
The metaverse is still in its nascent stages, and the technologies that will shape its construction are constantly evolving. Here are some exciting possibilities to consider:
-
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs): While still in their early stages, BCIs have the potential to revolutionize how we interact with the metaverse. Imagine controlling your avatar directly with your thoughts, eliminating the need for physical controllers or headsets. BCIs could create an even deeper sense of immersion and presence within the virtual world.
-
The Tactile Metaverse: The next frontier of immersion could lie in simulating touch beyond basic haptics. Imagine feeling the warmth of a virtual campfire or the texture of a virtual object with a degree of realism that rivals the physical world. Advances in material sciences and biomimetic technology could pave the way for a truly tactile metaverse experience.
-
The Evolving Role of Creators: The metaverse will require a vast array of content and experiences to keep users engaged. This presents a unique opportunity for creators – from 3D modelers and game developers to architects and fashion designers. Metaverse development tools will become more user-friendly, empowering individuals and communities to build and contribute to the virtual landscape.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of metaverse development is vast, there are significant challenges to consider:
-
Standardization: As mentioned earlier, open standards are crucial for creating a truly interconnected metaverse. Achieving consensus on these standards will be a complex undertaking, requiring collaboration between tech giants, startups, and regulatory bodies.
-
Privacy and Security: The vast amount of user data generated within the metaverse raises significant privacy concerns. Robust security measures will be essential to protect user data from breaches and exploitation. Additionally, ethical considerations regarding user behavior and content moderation within the metaverse will need to be addressed.
-
Accessibility: Equitable access to the metaverse is crucial. Not everyone can afford high-end VR headsets or powerful computers. Metaverse development services needs to be inclusive, ensuring that users with varying technological resources can still participate and enjoy the virtual world.
Conclusion:
Metaverse development is an ongoing process, and the technologies that will shape its construction are rapidly evolving. From real-time 3D engines and blockchain to AI and XR, the building blocks of the metaverse are coming together. As we move forward, a focus on open standards, ethical considerations, and accessibility will be paramount in creating a truly inclusive and immersive virtual world. The metaverse holds the potential to reshape how we work, play, and connect. By carefully constructing the metaverse with the right technologies and principles, we can build a digital future that benefits everyone.